Cholinergic Stimulation Will Produce Which of the Following Effects
Acetylcholine stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system helps contract smooth muscles dilate blood vessels increase secretions and slow the heart rate. However this response is minimal with injected cholinomimetic drugs.

Cholinergic Drugs Pharmacology Animation Youtube
Cholinergic antagonists also cause adverse effects.

. Cholinergic toxicity occurs when too much acetylcholine is present in the receptor synapse leading to excessive parasympathetic effects. Decr heart rate V. These effects include slowing of the heartbeat increases in normal secretions including the digestive acids of.
Rise in blood pressure. 1 stimulation of muscarinic receptor responses at autonomic effector organs. II III and IV only.
Strong cholinergic stimulation such as that which occurs from halothane and succinylcholine can produce profound bradycardia and reduce cardiac output in infants. The stimulation of cholinergic nerves to the penis causes an erection. A release of energy stores throughout the body.
Conversely the effects of inactivating cholinergic receptors include muscle relaxation heart rate acceleration pupil dilation mydriasis and lens flattening cyclopegia dryness of the upper airway of the respiratory system inhibition of tear production urine retention mouth dryness slowing down of mucociliary activity in the respiratory tract. Cholinergic stimulation will produce which of the following effects. Some cholinergic drugs such as muscarine pilocarpine and arecoline mimic the activity of acetylcholine in stimulating the parasympathetic nervous system.
A Acetylcholine produces the effects of parasympathetic stimulation whereas B Acetylcholine binds with adrenergic receptors whereas epinephrine binds with C Acetylcholine is released by adrenergic nerves whereas epinephrine is released by D Acetylcholine is released from the adrenal gland whereas epinephrine is released epinephrine produces the effects of. Stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system produces all of the following effects EXCEPT. These include drowsiness dry mouth excitability irritability loss of appetite nasal congestion throat irritation urinary incontinence and visual problems such as double vision or blurry vision.
This result is consistent with the purinergic nerve hypothesis. High potential for serious adverse effects. Cholinergic stimulation of rostral and caudal substantia nigra pars compacta produces opposite effects on circling behavior and striatal dopamine release measured by brain microdialysis.
A natural product found in certain mushrooms not used as a therapeutic drug. The effect of the cholinergic blockers on the stomach and intestines is decreased activity. Cholinergic drug any of various drugs that inhibit enhance or mimic the action of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine the primary transmitter of nerve impulses within the parasympathetic nervous system ie that part of the autonomic nervous system that contracts smooth muscles dilates blood vessels increases bodily secretions and slows the heart rate.
Increases in the heart rate and blood pressure. The contraction of the smooth muscle in various organs of the body gets mediated through M3 receptors. Divided into two subclasses- Direct acting-Bind to cholinergic receptors to produce the rest-and digest response and Indirect acting.
Dry mouth xerostromia Blurred vision cycloplegia Photophobia mydriasis Ganglion Blocking Drugs. Stimulation such as pinching of the skin has been shown to excite NBM cholinergic neurons 6 release ACh in the cortex 7 and consequently increase the cortical CBF 8. What are the physiological effects of cholinergic drugs.
Diversion of blood flow to the periphery of the body. Dilation of the bronchioles and pupils. Cholinergic muscarinic receptor stimulation produces the following effects except.
The cholinergic blockers produce specific effects on certain organs in the body. The cholinergic blockers produce a drying effect. 2 stimulation followed by paralysis of all autonomic ganglia and skeletal muscle.
For example sustained stimulation of cholinergic inputs in hippocampal slices resulted in an increase in the intrinsic excitability of dentate granule cells mediated by the long-term inhibition of a Kv7 current Martinello et al 2015. Muscarine is unable to produce the same result in the skeletal muscles or the nerves and muscles relating to the autonomic ganglia as the body does not naturally respond to cholinergic. The primary purpose of atropine in pediatric anesthesia is to protect against cholinergic stimulation.
Potentially the antcholiesterase agents can produce all of the following effects. And 3 stimulation with occasional subsequent depression of cholinergic receptor sites in the CNS. Following desensitisation of the excitatory P2-purinoceptors in the guinea-pig urinary bladder the excitatory responses to non-adrenergic non-cholinergic nerve stimulation were abolished while those to acetylcholine and histamine were little affected.
Effects of cholinergic stimulation. A quaternary amine that is a selective muscarinic agonist. Vasodilation of blood vessels- slower heart rate- constriction of bronchioles -increased secretion of mucus in the respiratory tracts-secretion of saliva.
These organs house receptors which are known to slow at the response of cholinergic stimulation and thus the medication is effective at enhancing this natural process in the body. Ganglionic blockers act mainly at the primary nicotinic-type cholinergic receptor at sympathetic and parasympathetic autonomic ganglia. Its secondary purpose is to inhibit the production of secretions.
I II III IV and V B. Acetylcholine stimulates muscarinic and nicotinic receptors to cause muscle contraction and glandular secretions. I III and V only C.
Recent studies have shown that microinjection of cholinergic agonists into the substantia nigra pars compacta increases dopamine release and turnover in the striatum of anesthetized rats. Inhibit the action of AchE. Cholinergic toxicity is caused by medications drugs and substances that stimulate enhance or mimic the.
Some Clitocybe species of mushrooms can produce potentially dangerous amounts of muscarine which can account for the symptoms observed by the Herbert family. Other forms of plasticity have also been linked to Kv7 channel expression. Incr mucus secretion III.
The effects of the cholinergic drugs are to produce the same effects as stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system. Sweat and tears- constriction of pupils.
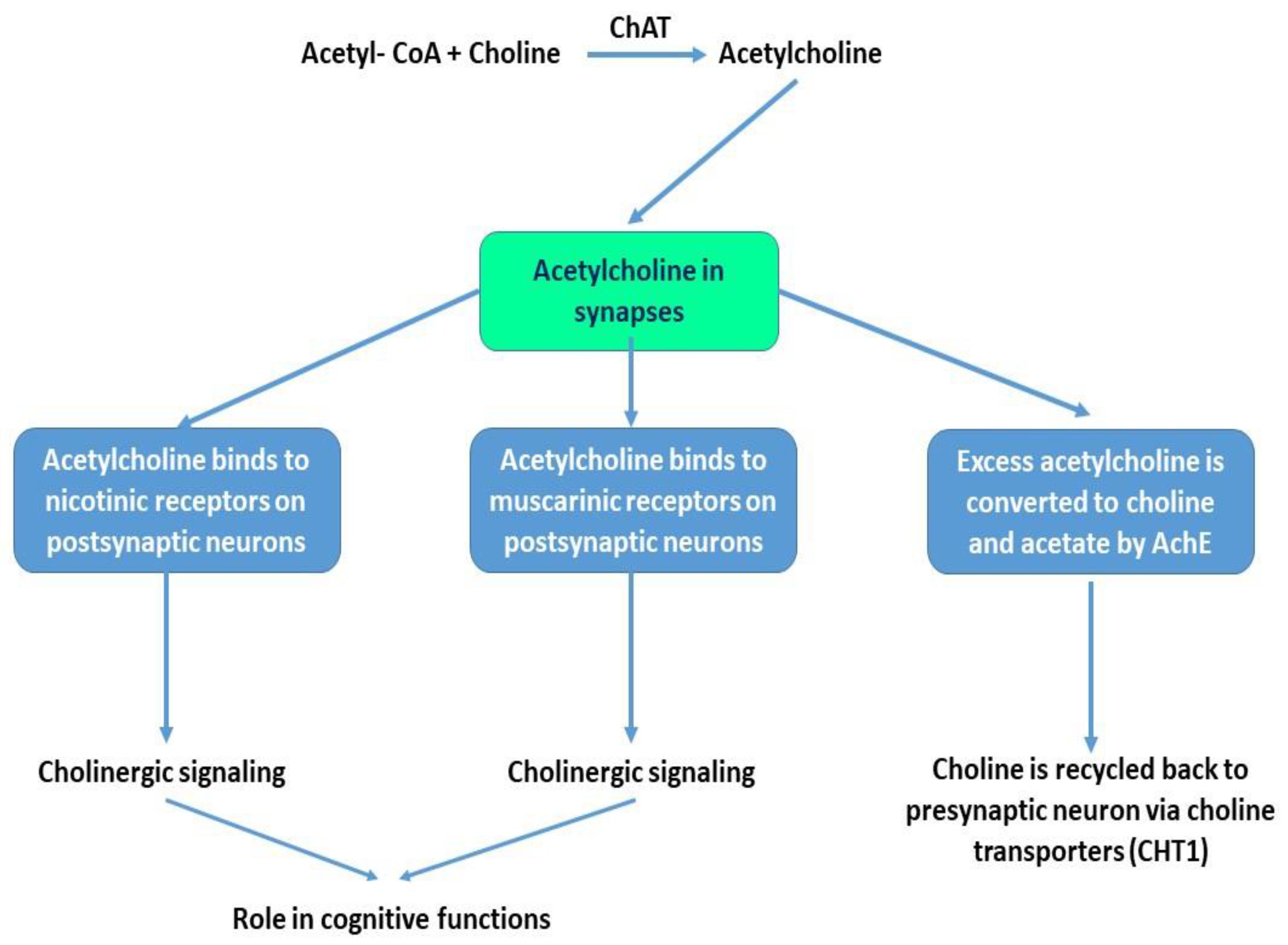
Ijms Free Full Text The Cholinergic System The Adrenergic System And The Neuropathology Of Alzheimer S Disease Html

Chemical Structures Of Neurotransmitters Compound Interest Chemical Structure Brain Chemistry Neurotransmitters

Cholinergic Anticholinergic Drugs Flashcards Quizlet

Pharmacological Blog Cholinergic Antagonists Cholinergic Pharmacology Nursing Pharmacological
0 Response to "Cholinergic Stimulation Will Produce Which of the Following Effects"
Post a Comment